Destination Management: Tourism Planning and Development:
- Share this post
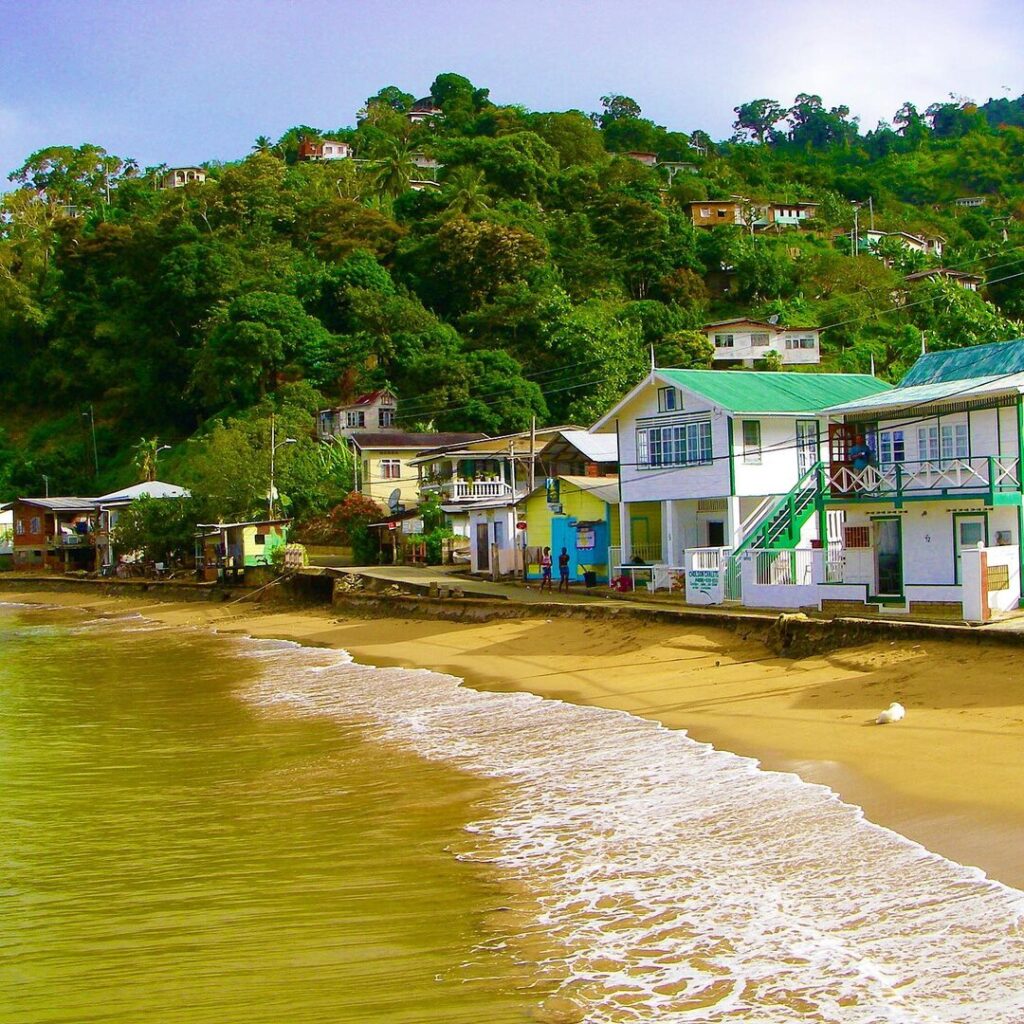
Photo Credit: The Seasoned Traveller, Charlotteville on Man O War Bay in Tobago
The Caribbean region, renowned for its pristine beaches, vibrant culture, and warm hospitality, attracts millions of tourists each year. However, managing tourism growth sustainably while preserving the natural and cultural assets of these destinations presents unique challenges. Today we will explore the intricacies of destination management in the Caribbean, highlighting key strategies for tourism planning and development.
1. Sustainable Tourism Practices:
Sustainability lies at the heart of effective destination management in the Caribbean. With fragile ecosystems and delicate cultural heritage, it’s essential to implement sustainable tourism practices to minimize environmental impact and ensure the long-term viability of these destinations. This includes promoting responsible tourism behaviours, conserving natural resources, supporting local communities, and mitigating the negative effects of tourism development.
2. Diversification of Tourism Offerings:
This includes developing niche tourism products such as ecotourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, and culinary tourism. By showcasing the unique cultural heritage and natural beauty of the region, destinations can attract visitors seeking authentic and immersive experiences beyond the beach resorts.
3. Infrastructure Development and Accessibility:
Investment in infrastructure and improving accessibility is crucial, this includes upgrading transportation networks, expanding airport facilities, enhancing cruise ship terminals, and providing reliable utilities and services. Improving connectivity within and between islands not only facilitates tourism growth but also benefits local residents by stimulating economic development and enhancing quality of life.
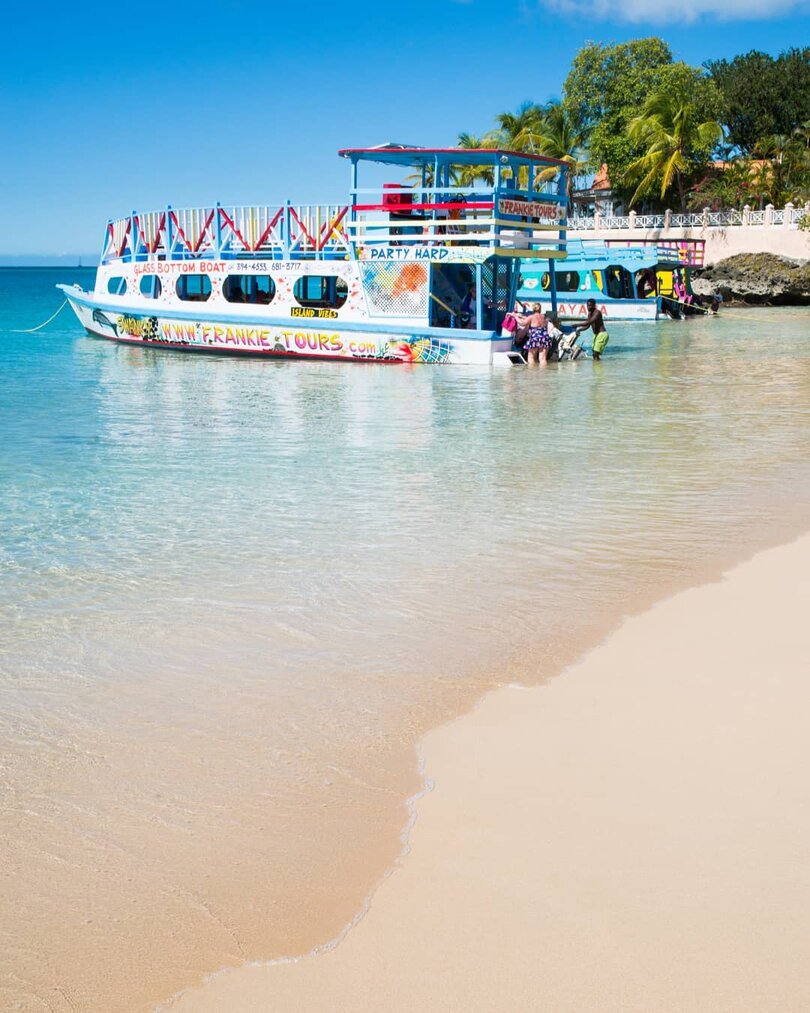
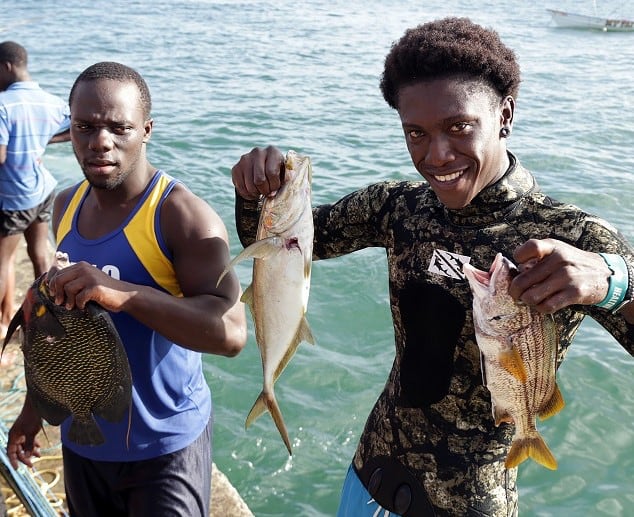






4. Community Engagement and Empowerment:
Community-based tourism initiatives empower residents to showcase their culture, traditions, and way of life while providing authentic experiences for visitors. By involving local stakeholders in planning and decision-making processes, destinations can foster a sense of ownership and promote sustainable development that benefits both residents and tourists.
5. Collaboration and Partnerships:
Collaboration and partnerships includes cooperation between governments, tourism authorities, private sector stakeholders, non-profit organizations, and local communities. By working together, stakeholders can leverage their resources, expertise, and networks to address common challenges, implement innovative solutions, and promote sustainable tourism development that balances economic growth with environmental and social responsibility.
Destination management is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful planning, collaboration, and commitment from all stakeholders. In the Caribbean, balancing tourism growth with environmental conservation, cultural preservation, and community empowerment is paramount to ensuring the long-term sustainability and resilience of these iconic destinations. By adopting sustainable tourism practices, diversifying tourism offerings, investing in infrastructure, engaging local communities, and fostering collaboration, the Caribbean can continue to thrive as a premier tourism destination for generations to come.
If you are interested in pursuing this professional path, discover more about our educational opportunities with our Hospitality Studies and Tourism Studies Associate degree programmes. Don’t miss out on the chance to turn your wanderlust into a thriving profession.
Enrol in our associate degree programmes and embark on a journey that blends education with adventure!
References:
- Hall, C. M., & Boyd, S. (Eds.). (2020). Tourism and Sustainable Development in the Caribbean: Contextualizing the SDGs. Routledge.
- Dodds, R., & Butler, R. W. (2021). Tourism Planning and Destination Management in a Changing World. CABI.
- Ritchie, J. R. B., & Crouch, G. I. (2003). The Competitive Destination: A Sustainable Tourism Perspective. CABI.
- Share this post
Upcoming Events:
Related Posts:
More You Might Like
Upcoming Short Courses:
- Lecturer: Maria Woods
- Online Classes, Face to Face
- 45 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: Ikeisha Niles
- Online Classes
- 30 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: Riyadh Mohammed
- Online Classes
- 6 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: Raakesh Madoo
- Face to Face
- TBD
- Coming Soon, Short Courses
- Lecturer: Raakesh Madoo
- Online Classes, Face to Face
- 30 hours
- Short Courses
Upcoming Courses:
- Lecturer: Chef Kwesi Selvon
- Face to Face
- 36 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: William Trim
- Face to Face
- 48 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: Chef Vergiss Lovelace
- Face to Face
- 6 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: Chef Sonia Phillip
- Face to Face
- 48 hours
- Short Courses
- Lecturer: Raakesh Madoo
- Online Classes, Face to Face
- 30 hours
- Short Courses